Kheel Plan 2 Seeks to Plug MTA Budget Gap
Ted Kheel and his band of transportation analysts are releasing an updated version of their low-cost transit proposal, which they are pitching as an alternative to the Ravitch Commission’s MTA rescue package. The revised Kheel Plan retains the original’s congestion zone cordon, charging vehicles to drive into Manhattan below 60th Street. The major twist is that drivers and subway riders would be charged variable-rate fees depending on the time of day (straphangers would only pay a fare during the morning and evening peaks).
I spoke to Kheel Planner Charles Komanoff about the new version, why politicians in Brooklyn and Queens should embrace it, and how it stacks up against the Ravitch Plan. We’ll post the interview later today. Follow the jump for the major points from Kheel Plan 2.
The promo flyer:
More from the press release:
Kheel’s plan, devised by a team of transportation planners and economists that Kheel has funded for nearly two years, contains these key elements:
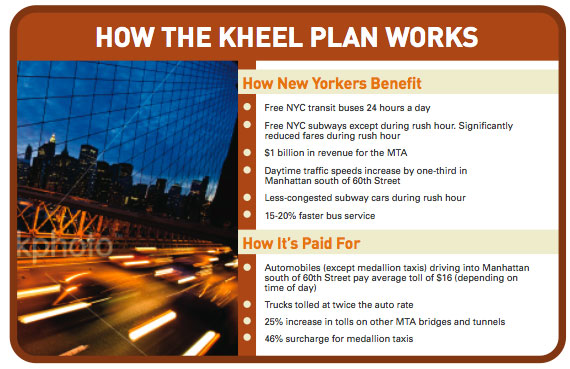
- A dramatic cut in subway fares (75% on average), including a complete fare elimination on weekends and holidays, overnight and mid-day,
- A variable fare during the weekday peak periods that’s lower than the current fare;
- Complete fare elimination on all NYC Transit buses at all times;
- Congestion pricing on car and truck traffic into the Manhattan Central Business District (CBD), with tolls varying sharply by time of day and averaging $16 per trip;
- A 46% surcharge on medallion taxi fares (note that medallion taxis, and no other vehicles, would be exempt from the congestion pricing charge);
- 25% higher tolls on MTA bridges that don’t directly access the Manhattan CBD.
Using their comprehensive proprietary model of the city’s transit system and road network, Kheel’s team concluded that the plan would:
- Yield over $1 billion in net revenue — sufficient to wipe out more than three-fourths of the MTA’s projected FY-2009 deficit;
- Increase overall subway ridership by 12% even as use of the system shrinks by 6% in the morning peak hour (8-9 a.m.) and 10% in the evening peak hour (5-6 p.m.);
- Raise traffic speeds in the chronically gridlocked CBD by one-third during the day and one-quarter overall, while also boosting travel speeds throughout the City.